Is a Root Domain Best for SEO?
When it comes to building a website and optimizing it for search engines, understanding the concept of root domains is essential. Root domains play a crucial role in web hosting, content management, and search engine optimization (SEO). Let’s explore what root domains are, their significance in SEO, and considerations for choosing the right root domain for your website.
In this article:
- Understanding Domain Structures
- Why Domain Structure Matters for SEO
- Advantages of Using a Root Domain
- Disadvantages of Using a Root Domain
- Subdomains vs. Subdirectories
- Root Domain Technical Considerations
- Disavowing Links
Understanding Domain Structures
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, it’s essential to understand what a root domain, subdomain, and subdirectory are:
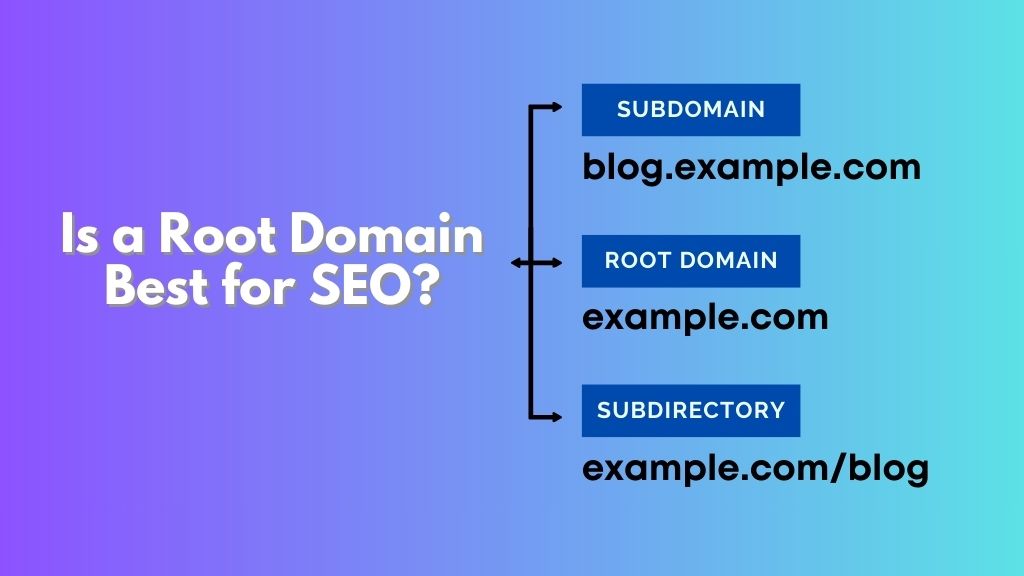
- Root Domain: This is your main website address, like example.com. It represents your primary domain without any prefixes.
- Subdomain: This is a subset of your main domain, such as blog.example.com or shop.example.com. Subdomains are treated as separate websites by search engines.
- Subdirectory: This is a folder within your main domain, like example.com/blog or example.com/shop. Subdirectories are seen as part of the main domain.
Why Domain Structure Matters for SEO
Search engines, like Google, use complex algorithms to rank websites. One of the factors they consider is how your website is structured. The domain structure can affect various SEO elements, including:
- Authority and Link Equity: Root domains typically have more authority than subdomains or subdirectories because all links point directly to the main domain.
- Crawl Efficiency: Search engines need to crawl your website to index it. The structure can impact how easily they can do this.
- Content Relevance: The way you organize content on your website can help search engines understand what your site is about, which affects rankings.
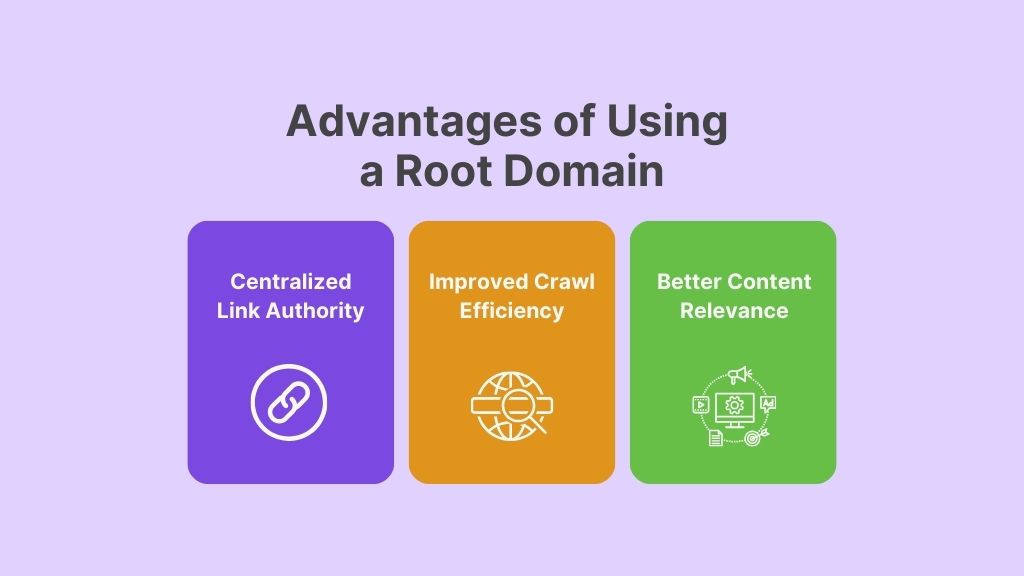
Advantages of Using a Root Domain
1. Centralized Link Authority
When you use a root domain, all backlinks (links from other websites to yours) contribute to the authority of your primary domain. This can significantly boost your SEO because search engines consider high-authority sites more trustworthy and relevant.
For example, if example.com has many backlinks, the authority of example.com increases, benefiting all pages under this domain. On the other hand, if you have blog.example.com as a subdomain, the backlinks to the blog might not benefit example.com directly.
2. Improved Crawl Efficiency
Search engines allocate a certain amount of crawl budget to each domain. A crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine will crawl on your site within a specific timeframe. By keeping everything under a root domain, you can ensure that search engines crawl your site more efficiently.
If your content is spread across subdomains, search engines might waste crawl budget crawling duplicate content or miss important pages. Keeping everything under the root domain helps avoid this issue.
3. Better Content Relevance
Using a root domain helps create a clear structure for your content. This organization helps search engines understand your content relevance to specific keywords. For example, if all your blog posts are under example.com/blog, it’s clear to search engines that this section is related to blog content.
Disadvantages of Using a Root Domain
While there are clear advantages, there are also potential downsides to consider:
1. Complexity in Management
Having all content under one root domain can make site and backlink management more complex, especially for large websites. It requires careful planning to ensure that the site remains organized and user-friendly.
2. Limited Keyword Targeting
Using a root domain might limit your ability to target specific keywords effectively. Subdomains can be optimized for different keywords without affecting the main domain. For instance, shop.example.com can target e-commerce-related keywords, while example.com can focus on broader topics.
Subdomains vs. Subdirectories
When deciding between subdomains and subdirectories, here are some factors to consider:
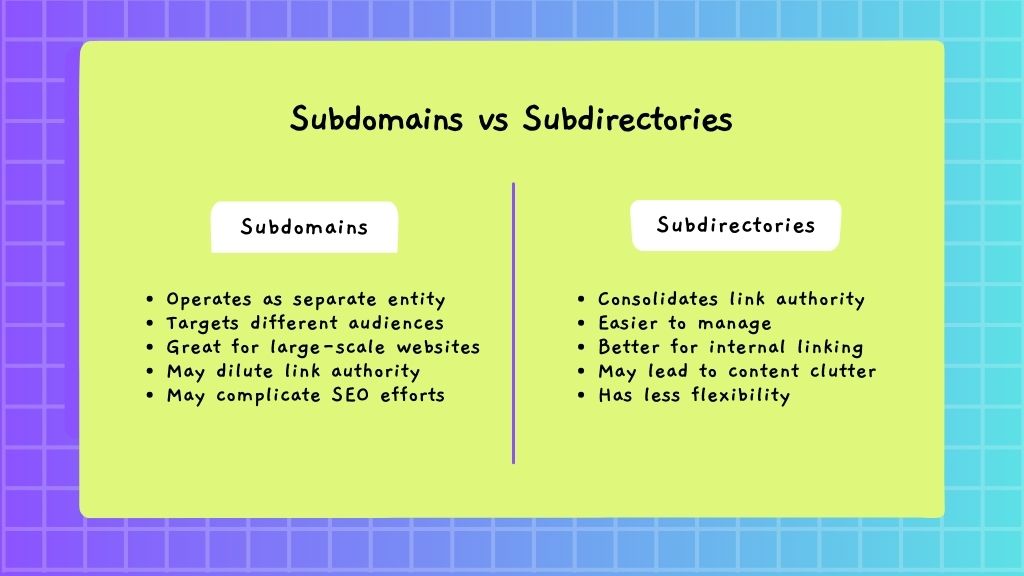
Subdomains
- Pros:
- Flexibility to operate as a separate entity.
- Useful for targeting different audiences or regions.
- Easier to manage large-scale websites with varied content.
- Cons:
- May dilute link authority.
- Search engines may treat them as separate websites, complicating SEO efforts.
Subdirectories
- Pros:
- Consolidates link authority under one root domain.
- Easier to manage SEO as a single entity.
- Better for internal linking and crawl efficiency.
- Cons:
- Can become cluttered and harder to manage as content grows.
- Less flexibility compared to subdomains.
Root Domain Technical Considerations
Setting Up a Root Domain
To maximize SEO benefits from a root domain, ensure you:
- Implement SSL: Use HTTPS to secure your website. This is a ranking factor for Google.
- Optimize Site Speed: A fast-loading site improves user experience and SEO.
- Use Canonical Tags: Prevent duplicate content issues by specifying the preferred version of a page.
- Set Up 301 Redirects: Redirect old pages to new ones to maintain link equity.
Managing Subdomains
If you opt for subdomains, consider these tips:
- Treat Subdomains as Separate Sites: Optimize each subdomain individually.
- Use Consistent Branding: Maintain a consistent brand image across subdomains.
- Track Performance Separately: Use analytics tools to track each subdomain’s performance.
Handling Subdirectories
For subdirectories, follow these practices:
- Create a Logical Structure: Organize content in a way that makes sense to users and search engines.
- Optimize Internal Linking: Use internal links to help search engines and users navigate your site.
- Monitor Crawl Budget: Use tools like Google Search Console to ensure search engines are crawling important pages.
Disavowing Links
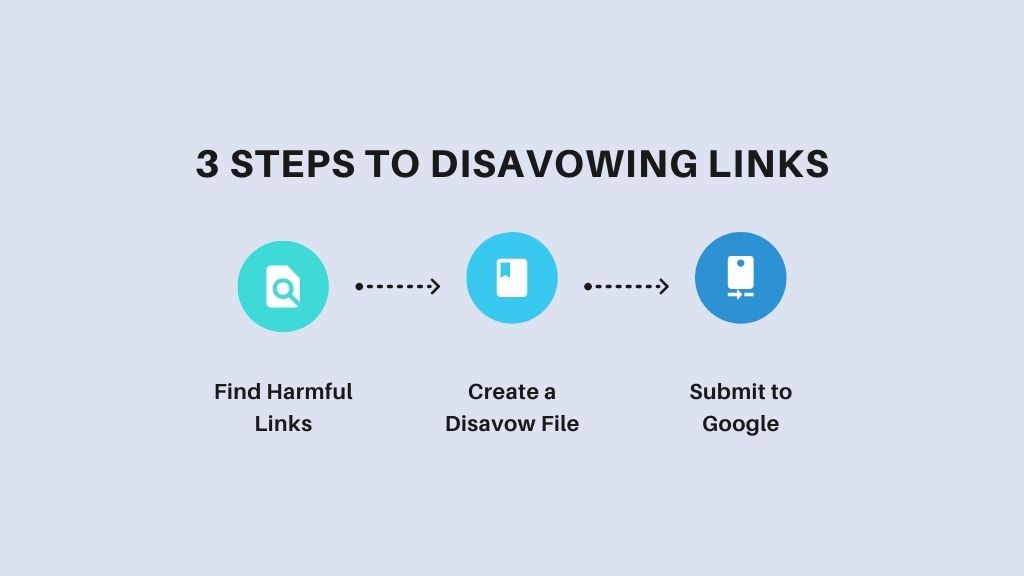
Disavowing links is an advanced SEO technique used to tell search engines to ignore certain backlinks. This can be crucial if you have bad or spammy links pointing to your site. Here’s how to handle disavowing links effectively:
- Identify Harmful Links: Use tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find toxic backlinks.
- Create a Disavow File: List all harmful links in a text file.
- Submit to Google: Upload the disavow file to Google Search Console.
Why Disavowing Links Matters
Bad backlinks can really hurt your website’s SEO. Think of backlinks like votes of confidence from other websites. If a good, high-quality site links to yours, it’s like they’re saying, “This site is trustworthy and has great content.” But if spammy, low-quality sites link to yours, it sends the opposite message.
Search engines, like Google, might think your site is also spammy if it has too many bad backlinks. This can lead to penalties, which means your site might rank lower in search results or, in extreme cases, be removed from search results entirely. Disavowing these bad links tells search engines to ignore them, helping you keep your site’s SEO in good shape.
Best Practices for Disavowing Links
Regularly Audit Backlinks
You should regularly check the backlinks to your site to spot any harmful ones early. Use tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to monitor who is linking to you. By keeping an eye on this, you can quickly catch any bad links before they cause too much damage.
Disavow with Caution
When you disavow links, be very careful. Only disavow links that are truly harmful. If you mistakenly disavow good links, it can hurt your SEO because you’ll be throwing away good “votes of confidence.” Always double-check the links you plan to disavow to make sure they’re really bad.
Keep a Backup
Always keep a backup of your disavow file. This file lists all the links you want search engines to ignore. By having a backup, you can easily refer back to it if needed or restore it if something goes wrong. It’s a safety net that ensures you don’t lose track of the harmful links you’ve already disavowed.
What’s Best for Your SEO?
In the debate of whether a root domain is better for SEO, the answer depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Root domains generally offer better link authority, crawl efficiency, and content relevance. However, subdomains provide flexibility and can be beneficial for targeting different keywords and audiences.
When choosing the right structure for your website, consider the pros and cons of each option. By understanding the technical aspects and best practices outlined in this article, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your SEO goals.
Remember, SEO is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Continuously monitor your site’s performance and be ready to adapt your strategy as needed to achieve the best results.
Aside from choosing the right domain structure, it’s also important to do outreach and drive traffic to your website. Whether you’re a blog writer needing to remove barriers in your outreach plan or a small business owner looking to scale efficiently, Link Genius provides the tools and systems to build authority and streamline your processes.
Join us today and see how our tool can help your domain rank better in search.
