404 Error Management: How to Handle Lost Pages

Managing 404 errors is an essential part of maintaining a healthy and user-friendly website. A 404 error occurs when a page on your website cannot be found, leading to a frustrating experience for your visitors.
If not handled properly, 404 errors can hurt your website’s SEO, reduce user satisfaction, and even cause you to lose potential customers. Let’s explore what 404 errors are, why they matter, and provide actionable steps to manage and fix them effectively.
In this article:
- What Is a 404 Error?
- Why 404 Errors Matter
- How to Identify 404 Errors
- Best Practices for Handling 404 Errors
What Is a 404 Error?
A 404 error, also known as a “Page Not Found” error, occurs when a web server cannot find the page that a user is trying to access. This usually happens when the page has been deleted or moved or the URL has been mistyped.
How 404 Errors Happen
404 errors can occur for a variety of reasons:
- Deleted Pages: If a page is removed from your website without proper redirection, users trying to access it will encounter a 404 error.
- Broken Links: Internal or external links that point to non-existent pages will result in 404 errors.
- Typos in URLs: If users or search engines attempt to visit a mistyped URL slug, they will be directed to a 404 page.
- Server Issues: Sometimes, server misconfigurations can cause pages to return 404 errors, even if they exist.

Why 404 Errors Matter
Impact on User Experience
404 errors can be frustrating for users. When visitors encounter a 404 error, they are likely to leave your site and look elsewhere for the information they need. This results in a poor user experience and can decrease the likelihood of direct traffic returning to your site in the future.
SEO Implications
Search engines, like Google, do not favor websites with many 404 errors. If your site has a high number of broken links or missing pages, it can negatively impact your SEO rankings. This can reduce your visibility in search engine results and lead to a loss of organic traffic.
Loss of Potential Customers
If a user encounters a 404 error when trying to access an important page, such as a product page or contact form, you could lose a potential customer. Ensuring that your website is free from broken links and missing pages is crucial for maintaining your business’s online reputation.

How to Identify 404 Errors
Use Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool that helps you monitor and maintain your website’s presence in Google search results. It provides valuable insights into how your site is performing and can alert you to any 404 errors that Google’s crawlers encounter.
Set Up Monitoring Tools
Various tools can help you identify 404 errors on your website. Tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, and SEMrush can crawl your site and generate reports on broken links, missing pages, and other SEO issues.
Check Server Logs
Your web server logs can provide detailed information about every request made to your server, including 404 errors. Reviewing these logs can help you identify patterns and determine the cause of 404 errors.
Use Analytics
Google Analytics and other analytics platforms can also be used to track 404 errors. By setting up custom reports or using the Behavior Flow tool, you can see where users encounter 404 errors and how they interact with your site after encountering them.

Best Practices for Handling 404 Errors
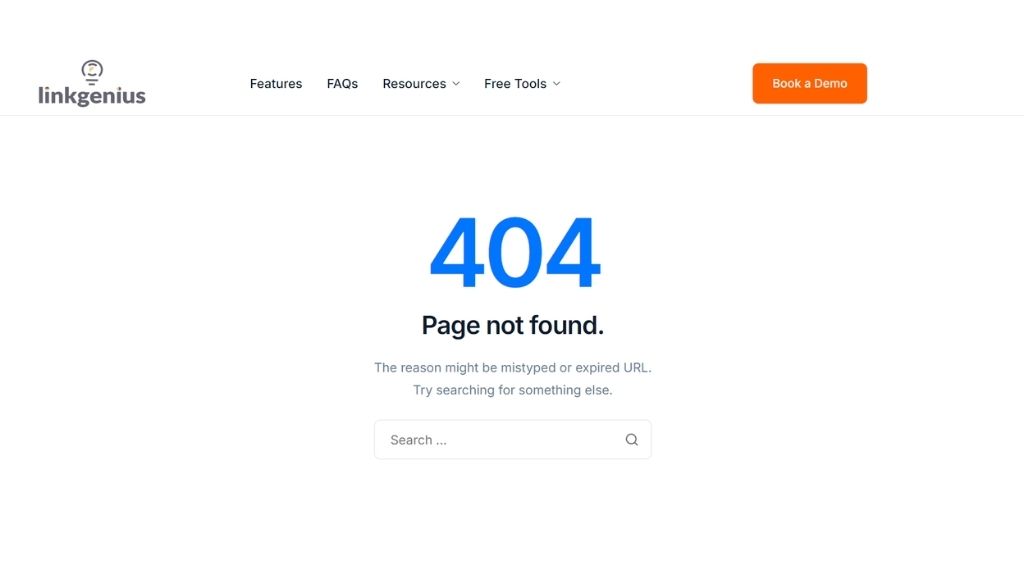
1. Create a Custom 404 Error Page
A custom 404 error page can turn a negative experience into a positive one. Instead of showing a generic “Page Not Found” message, a custom 404 page can guide users back to useful content on your site.
What to Include on a Custom 404 Page
- Friendly Message: Explain that the page they are looking for cannot be found and apologize for the inconvenience.
- Search Bar: Include a search bar to help users find the content they are looking for.
- Links to Popular Pages: Provide links to your homepage, blog, or other popular sections of your website.
- Navigation Menu: Ensure that your site’s main navigation menu is available on the 404 page so users can easily find their way around.
- Branding: Keep the design of your 404 page consistent with the rest of your website to maintain a cohesive user experience.
2. Implement 301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect from one URL to another. It tells search engines that a page has moved permanently, and they should transfer the SEO value from the old page to the new one.
When to Use 301 Redirects
- Deleted Pages: If you delete a page, set up a 301 redirect to guide users to a relevant alternative page.
- Changed URLs: If you change a page’s URL, use a 301 redirect to ensure that users and search engines are redirected to the new URL.
- Broken Links: For links that lead to 404 errors, create 301 redirects to the correct or relevant pages.
How to Set Up 301 Redirects
You can set up 301 redirects using your website’s .htaccess file (for Apache servers), through your content management system (CMS), or by using a plugin like Yoast SEO (for WordPress sites). Be sure to test the redirects to ensure they are working properly.
Other HTTP status codes you might encounter include the 409 conflict error, which occurs when there’s a conflict between the request and the current state of the resource, often due to a version control issue.
307 redirects and 302 redirects are temporary redirects that tell the browser the requested resource has moved temporarily, but will be back at the original URL later. Meanwhile, the 304 status code indicates that the content has not changed since the last time it was requested, so the browser can load it from the cache instead of downloading it again.
3. Audit Your Website Regularly
Regular website audits help you catch 404 errors before they impact users and SEO. An audit allows you to identify broken links, missing pages, and other issues that could lead to 404 errors.
Tools for Auditing
Use tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to conduct a comprehensive audit of your site. These tools can crawl your website and generate reports on any issues that need attention.
Steps to Audit Your Site
- Crawl Your Website: Use an SEO tool to crawl your site and identify any 404 errors or broken links.
- Review Reports: Analyze the reports to understand the scope of the issues and which pages are affected.
- Fix Errors: Implement 301 redirects, update links, or restore missing content as needed.
- Monitor Changes: After making changes, monitor your site to ensure that the errors have been resolved.
4. Update Internal Links
Internal links help users navigate your site and allow search engines to discover and index your content. Broken internal links can lead to 404 errors, which disrupt the user experience and negatively impact SEO.
How to Manage Internal Links
- Use Relative URLs: Using relative URLs (e.g., “/about-us” instead of “www.example.com/about-us”) can prevent issues if your domain changes.
- Regularly Check Links: Use tools to regularly check for broken internal links and update them as needed.
- Organize Content: Ensure that your content is well-organized and that all internal links lead to relevant, live pages.

5. Update External Links
External links from other websites to your site can also cause 404 errors if the destination pages are deleted or moved. Monitoring and managing these links helps maintain your site’s SEO health.
How to Handle External Links
- Reach Out to Webmasters: If you notice that an external link is pointing to a missing page, contact the webmaster of the referring site and request an update to the link.
- Create Redirects: If possible, create 301 redirects for missing pages that are still receiving external links.
- Disavow Toxic Links: For links from low-quality or spammy sites, consider using Google’s disavow tool to prevent them from negatively impacting your SEO.
6. Opt for the “410 Gone” Status Code
A “410 Gone” status code indicates that a page has been permanently removed and will not be replaced. Unlike a 404 error, which suggests that a page might return, a 410 status code tells search engines that the page is gone for good.
When to Use a 410 Status Code
Use a 410 status code if you permanently remove content from your site and do not intend to replace it. This helps search engines quickly remove the page from their index, preventing it from showing up in search results.
How to Implement a 410 Status Code
Implement a 410 status code through your website’s .htaccess file or by using a plugin or CMS feature. Be sure to test the status code to ensure it’s working correctly.
7. Monitor Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a powerful tool for monitoring your website’s health and performance. It alerts you to any 404 errors and other issues that could impact your SEO.
How to Use Google Search Console for 404 Management
- Check Crawl Errors: Regularly review the Crawl Errors report in Google Search Console to identify any 404 errors.
- Fix Issues Promptly: Address any 404 errors identified by Google Search Console as soon as possible.
- Resubmit Fixed URLs: After fixing 404 errors, resubmit the affected URLs to Google for reindexing.
8. Track User Behavior
Tracking user behavior on your site can provide insights into how 404 errors impact their experience. Understanding how users interact with your 404 pages can help you improve your error management strategy.

Tools for Tracking Behavior
Use tools like Google Analytics, Hotjar, or Crazy Egg to track how users behave when they encounter a 404 error. These tools can show you where users click, how long they stay on the page, and whether they navigate to other parts of your site.
How to Improve Based on Behavior
- Improve 404 Pages: If users are leaving your site after encountering a 404 error, consider enhancing your custom 404 page with more helpful links and options.
- Redirect Based on Behavior: If users frequently land on a specific 404 page, consider creating a redirect to a relevant page that meets their needs.
9. Keep an Eye on Your Competitors
Monitoring your competitors’ websites can give you insights into how they handle 404 errors and site maintenance. Learning from their strategies can help you improve your own site.
How to Analyze Competitors
- Visit Competitor Sites: Manually visit your competitors’ websites and look for any 404 errors or issues with site navigation.
- Use Tools: Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to analyze your competitors’ backlink profiles and identify any broken links they might have.
- Benchmark Your Site: Compare your site’s 404 error management to your competitors and identify areas for improvement.
Focusing on User Experience
Effectively managing 404 errors is crucial for maintaining a high-quality website that provides a positive user experience and performs well in search engine rankings. By identifying and fixing 404 errors promptly, creating custom 404 pages, implementing 301 redirects, and regularly auditing your site, you can minimize the impact of these errors on your users and your SEO.
User experience also plays a role in your outreach efforts. As you work on improving your site’s error management, use Link Genius to enhance your backlink strategy. Book a demo today!
